Abstract
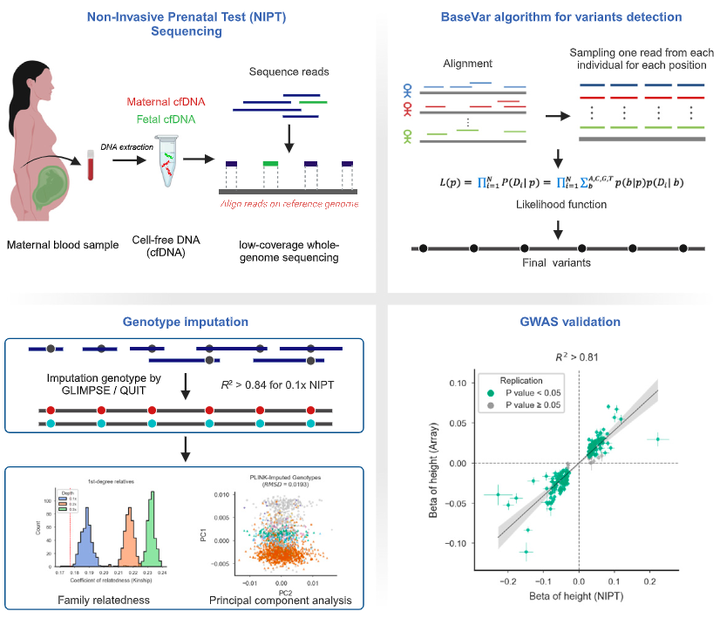
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) employs ultra-low-pass sequencing of maternal plasma cell-free DNA to detect fetal trisomy. Its global adoption has established NIPT as a large human genetic resource for exploring genetic variations and their associations with phenotypes. Here, we present methods for analyzing large-scale, low-depth NIPT data, including customized algorithms and software for genetic variant detection, genotype imputation, family relatedness, population structure inference, and genome-wide association analysis of maternal genomes. Our results demonstrate accurate allele frequency estimation and high genotype imputation accuracy (𝑅2>0.84) for NIPT sequencing depths from 0.1× to 0.3×. We also achieve effective classification of duplicates and first-degree relatives, along with robust principal-component analysis. Additionally, we obtain an 𝑅2>0.81 for estimating genetic effect sizes across genotyping and sequencing platforms with adequate sample sizes. These methods offer a robust theoretical and practical foundation for utilizing NIPT data in medical genetic research.